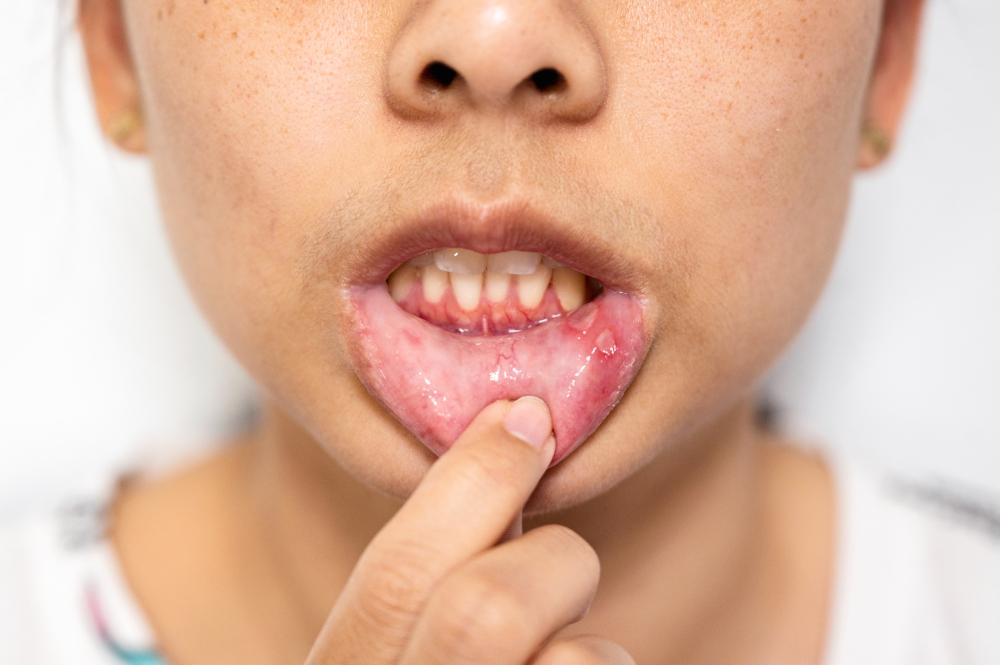
Bleeding Gums: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Bleeding gums are a common oral health concern that many people experience at some point in their lives. While it might seem like a minor issue, bleeding gums at the gumline can be a sign of underlying gingival health problems that require attention. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about bleeding gums, including the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures you can take to maintain healthy gums and a beautiful smile.
What Are Bleeding Gums?
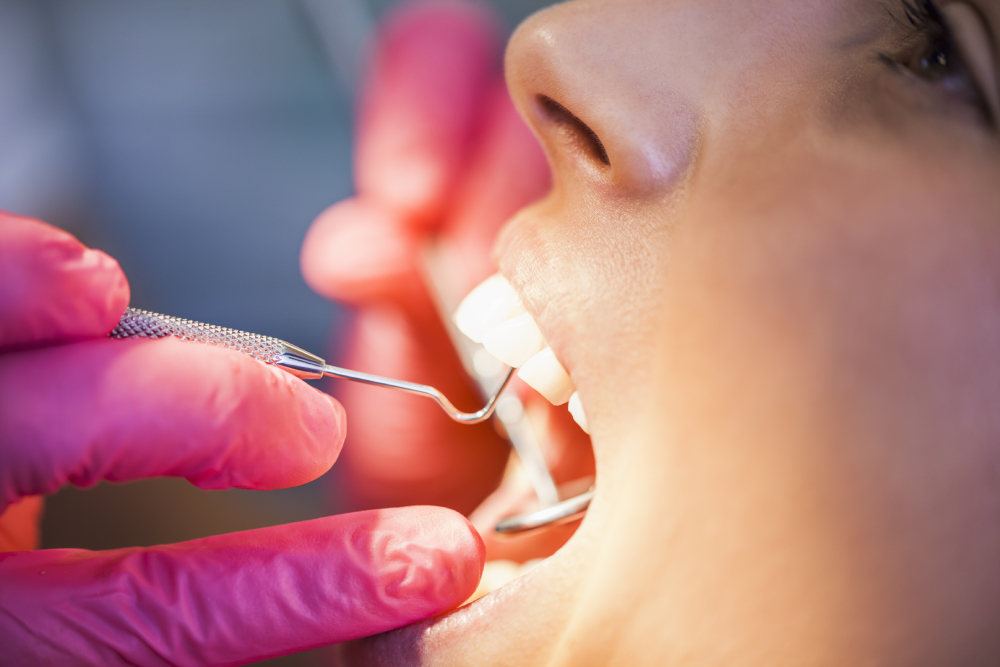
Understanding the Basics
Bleeding gums occur when the gum tissue becomes inflamed and starts to bleed, usually during brushing or flossing. Gums that bleed are often a sign of gum disease, but they can also indicate other health issues. The severity of the bleeding, an oral health issue, can range from a few spots of blood on your toothbrush to more significant bleeding that requires immediate attention.
Why Do Gums Bleed?
Gums are made up of soft tissue that surrounds and protects your teeth. When this tissue becomes irritated or damaged, it can lead to inflammation and bleeding. While occasional bleeding, sensitive gums, or pregnancy might not be a cause for concern, frequent or heavy bleeding should be evaluated by a dentist or healthcare professional.

Causes of Bleeding Gums
Gingivitis: The Most Common Cause
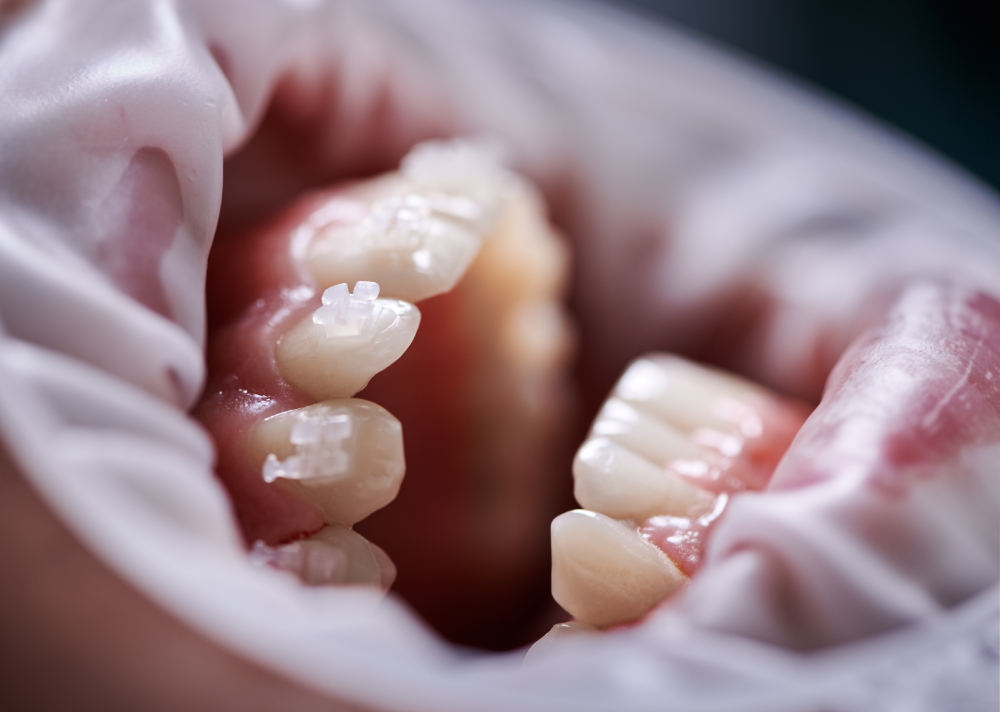
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and the most common cause of bleeding gums. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on your teeth and irritates the gums. Plaque forms when food particles mix with saliva and bacteria in the mouth, and if not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar. Tartar is more difficult to remove and can lead to more serious gum issues, bleeding gums treatment.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
- Red, swollen gums
- Tenderness in the gums
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
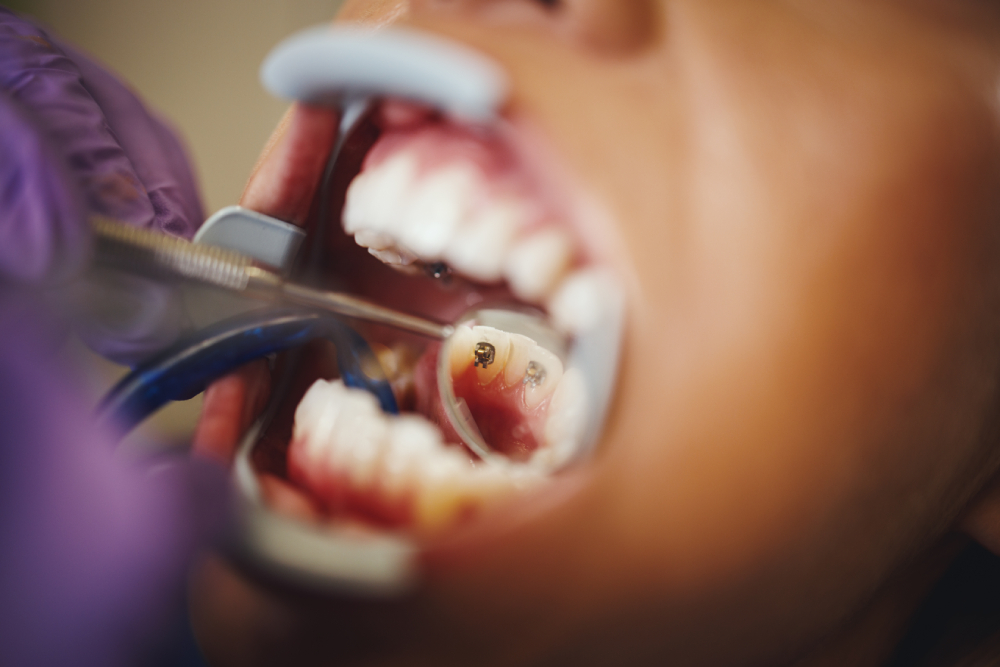
Periodontitis: When Gingivitis Advances
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis causes the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets that become infected. As the body fights the infection, the tissues and bone that hold the teeth in place can break down, leading to tooth loss.
Other Causes of Bleeding Gums
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can lead to plaque buildup and gum irritation.
- Improper Brushing Technique: Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with stiff bristles can damage your gums.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase the likelihood of gum bleeding.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins like vitamin C and vitamin K can make your gums more prone to bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco products can irritate the gums and contribute to gum disease, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Systemic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, leukemia, or blood clotting disorders can also lead to bleeding gums.
Symptoms Associated with Bleeding Gums

Signs to Watch For
While bleeding gums are a symptom in themselves, they often come with other signs that indicate underlying issues. Recognizing these symptoms, like sensitive gums during pregnancy, can help you take action early and prevent more serious dental problems.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Also known as halitosis, bad breath can accompany bleeding gums and is often a sign of gum disease.
- Swollen or Puffy Gums: Swelling is a common indicator of inflammation and gum disease.
- Receding Gums: Gums that appear to be pulling away from the teeth may indicate periodontitis.
- Loose Teeth: If your teeth feel loose, it could be a sign that the supporting structures are compromised.
- Discomfort or Pain: Soreness or pain in the gums, especially when eating or brushing, can signal gum disease or other dental issues.
Diagnosing Bleeding Gums
When to See a Dentist
If you notice your gums bleeding regularly, it’s essential to see a dentist for a proper diagnosis. Early detection of gum disease or other underlying issues can prevent more severe complications.
Dental Examination
During a dental exam, your dentist will check for signs of gum disease, such as plaque buildup, tartar, swelling, and gum recession. They will also ask about your oral hygiene routine, any medications you’re taking, your overall health, and sensitive gums during pregnancy.
X-Rays
X-rays may be necessary to assess the extent of gum disease, particularly if periodontitis is suspected. X-rays can show the condition of the bone surrounding your teeth and whether there has been any bone loss.
Blood Tests
In some cases, if your dentist suspects that a systemic condition like diabetes or a blood clotting disorder might be contributing to your bleeding gums, they may recommend blood tests to check for underlying health issues.
Treatment Options for Bleeding Gums

Improving Oral Hygiene
The first step in treating bleeding gums is improving your oral hygiene routine. Brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease. Using an antibacterial mouthwash can also reduce the bacteria that cause gum inflammation.
Professional Dental Cleaning
A professional dental cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, is essential for removing tartar buildup that can’t be removed with regular brushing and flossing. This procedure involves cleaning below the gumline to remove plaque and tartar and smoothing the roots of the teeth to prevent future buildup.

Medications
If you have gum disease, your dentist may prescribe medications to help control the infection and reduce inflammation. These may include:
- Antibiotic Mouthwash: To reduce bacteria and plaque.
- Topical Antibiotics: Applied directly to the gums or inserted into gum pockets.
- Oral Antibiotics: In severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to treat gum infections.
Surgical Treatments
In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical intervention may be necessary to restore gum health and prevent tooth loss. Surgical options include:
- Flap Surgery: The gums are lifted back, and tartar is removed from deeper pockets. The gums are then stitched back in place to fit snugly around the teeth.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts: If you’ve experienced significant bone or gum loss, grafts can help regenerate the lost tissue. Bone grafts use natural or synthetic bone to replace the lost bone, while soft tissue grafts can reinforce thin or receding gums.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This procedure encourages bone growth in areas where it has been destroyed by bacteria. A mesh-like material is inserted between the bone and gum tissue to keep the gum tissue from growing into the area where the bone should be.
Preventing Bleeding Gums
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
The most effective way to prevent bleeding gums is to maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, and don’t forget to floss daily. Regular use of an antiseptic mouthwash can also help keep your gums healthy by reducing bacteria and plaque.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial for preventing gum disease. Your dentist can remove tartar buildup, check for early signs of gum disease, and provide guidance on maintaining good oral hygiene.
Eat a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health, including gum health. Make sure to include plenty of vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, strawberries, and leafy greens in your diet. Vitamin C is essential for healthy gums, as it helps repair and maintain gum tissue. Additionally, foods high in vitamin K, such as spinach, kale, and broccoli, can help improve blood clotting and reduce gum bleeding.
Avoid Tobacco Products
Smoking and the use of other tobacco products can significantly increase your risk of gum disease and bleeding gums. Quitting smoking can have immediate and long-term benefits for your oral and overall health.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections like gum disease. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help keep your gums healthy.
Be Aware of Medication Side Effects
If you’re taking medication that increases your risk of bleeding gums, such as blood thinners, talk to your doctor or dentist. They may be able to adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments that are gentler on your gums.
Complications of Untreated Bleeding Gums
Progression to Periodontitis
If left untreated, bleeding gums can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss. Periodontitis not only affects your oral health but can also have systemic consequences, as the bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream and affect other parts of the body.
Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Research has shown a link between gum disease and heart disease. The inflammation caused by gum disease may contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions by allowing harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream and travel to the heart.
Diabetes Complications
Gum disease can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels, leading to complications for people with diabetes. Conversely, high blood sugar levels can contribute to the development and progression of gum disease, creating a vicious cycle. Managing both gum health and blood sugar levels is essential for overall well-being.
Pregnancy Complications
Pregnant women with gum disease are at a higher risk of complications such as preterm birth and low birth weight. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make gums more susceptible to inflammation and bleeding, making it crucial for pregnant women to maintain good oral hygiene and seek regular dental care.
When to See a Dentist
Recognizing the Signs
If you experience frequent or severe gum bleeding, it’s essential to seek professional dental care. Other signs that warrant a visit to the dentist include persistent bad breath, swollen or tender gums, receding gums, and loose teeth. Early intervention can prevent more serious complications and help you maintain a healthy smile.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums are a common but potentially serious issue that should not be ignored. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bleeding gums can help you take proactive steps to maintain good oral health. By practicing good oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and addressing any underlying health conditions, you can prevent and manage bleeding gums effectively. If you’re experiencing bleeding gums, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice and take action to protect your oral health.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common cause of gum bleeding?
Gum bleeding is most commonly caused by a buildup of plaque around the gum line due to improper tooth brushing techniques or frequencies.
Can bleeding gums affect health?
There are studies to show that bleeding gums can potentially affect your heart as the bloodstream can potentially transfer bacteria from your gums to the heart. It may also be a sign that you may have underlying medical conditions or nutritional deficiencies.
Can stress cause bleeding gums?
Yes, stress can potentially cause your gums to bleed due to hormonal imbalances or vitamin deficiencies.
What deficiency causes bleeding gums?
A deficiency in Vitamin C, Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D may cause bleeding gums. A deficiency in Zinc may also precipitate bleeding gums.
What causes gum bleeding and sensitivity?
Gum bleeding is usually caused by a buildup of plaque around the gum line leading to an irritation of the gums. This may lead to bleeding of the gums and sensitivity. Sensitivity may also be caused by excessively hard toothbrushing techniques. Sometimes, deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals may also cause bleeding and sensitivity.
What causes gums to bleed at night?
A buildup of plaque around the gums may cause irritation of the gums which may bleed on touch.
What are the possible complications of gum bleeding?
There are studies that show a link between the heart and gum disease so bacteria from bleeding gums can potentially affect the heart. Progression of gum disease may also cause bone loss around the affected teeth, loosening and pain of the teeth.
How is gum bleeding managed?
If detected early, scaling to remove plaque and calculus will help to remove the bacteria that irritates the gums and causes bleeding gums. Sometimes more severe cases may need root planing or deep cleaning which is effective at removing the bacteria causing bleeding gums.
